Gum disease affects more than a billion people worldwide, often progressing silently until it causes significant damage to the teeth’s supporting structures. When advanced periodontal disease creates deep pockets between the teeth and gums, patients require surgical intervention. Pocket reduction surgery, or osseous surgery, is a powerful weapon against periodontal disease.
As dental professionals, we understand that many patients feel anxious when they hear the word “surgery.” That’s why we’re sharing everything you need to know about pocket reduction procedures to help you make informed decisions about your periodontal health.
Understanding Periodontal Pockets
Healthy gums fit snugly around each tooth, creating a protective seal that keeps bacteria from reaching the deeper structures. The space between your tooth and gum tissue normally measures between 1 and 3 millimeters deep. However, when bacteria accumulate and cause inflammation, these spaces can deepen into “pockets.”
These pockets create the perfect environment for harmful bacteria to thrive. The resulting bacterial colonization leads to continued tissue inflammation and destruction, progressive bone loss around the teeth, increased risk of tooth mobility, and eventual tooth loss. Research also links advanced periodontal disease to various systemic health complications, making treatment even more critical.
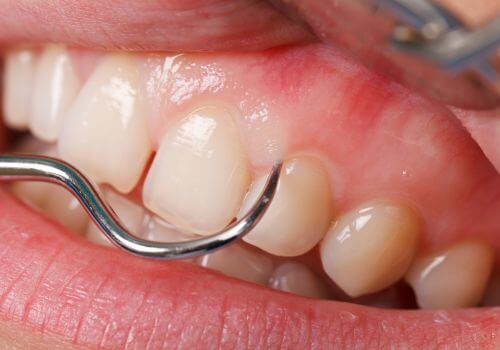
What Makes Pocket Reduction Surgery Necessary?
When periodontal pockets exceed 5 millimeters in depth, they become challenging to clean with regular oral hygiene, and even professional cleanings may not effectively remove bacteria.
In cases of advanced periodontal disease, conservative treatments like scaling and root planing may not be enough. Pocket reduction surgery becomes a crucial step in eliminating bacterial infections, reducing pocket depth, preserving teeth, and restoring overall periodontal health.
The Pocket Reduction Procedure
The first step in the process is a comprehensive pre-surgical assessment, which includes periodontal charting, digital radiographs to evaluate bone levels, a review of the patient's medical history, and a discussion of treatment goals and expectations.
The surgery itself follows a precise sequence. First, the area is numbed with local anesthesia to ensure the patient’s comfort. The oral surgeon then makes small incisions along the gumline to lift the tissue, providing direct access to the teeth, roots, and surrounding bone.
Next, specialized instruments are used to remove calculus, plaque, and diseased tissue from the root surfaces. The surgeon will then reshape any irregular bone surfaces to promote better tissue reattachment and healing. Finally, the gum tissue is repositioned and secured with tiny sutures, often resulting in a slightly lower gum line that allows for easier cleaning and maintenance.
Recovery and Healing
In the immediate postoperative period (the first 24 to 48 hours after surgery), most patients experience mild discomfort that’s manageable with over-the-counter pain medication. Minor swelling usually peaks around day two or three, and bleeding subsides within a few days.
During the first week, patients should stick to a soft diet and practice gentle oral hygiene. Most surgeons prescribe an antimicrobial mouth rinse and schedule a follow-up appointment for suture removal. Long-term recovery involves gradually returning to regular oral hygiene routines, progressive tissue healing over several weeks, and regular maintenance appointments.
Benefits of Pocket Reduction Surgery
This procedure offers numerous advantages for patients with advanced periodontal disease. From a health perspective, the surgery eliminates bacterial reservoirs, reduces inflammation throughout the mouth, prevents further bone loss, and enhances the ability to maintain proper oral hygiene.
Aesthetic improvements include better gum contours, reduced likelihood of root exposure, more symmetrical gum lines, and improved smile appearance. The long-term advantages include increased probability of keeping natural teeth, lower risk of systemic health complications, reduced need for future dental work, and better oral health predictability.
Success Factors and Modern Approaches
Several elements influence the outcome of pocket reduction surgery. Patient-related factors include commitment to good oral hygiene, smoking cessation, management of systemic conditions, and compliance with post-operative instructions. Clinical considerations include initial pocket depths, amount of remaining bone support, and quality of surgical technique.
Technological advances have made modern pocket procedures more effective and efficient than ever before. Digital planning now includes 3D imaging for precise surgical planning and computer-guided tissue mapping. In addition, advanced instruments, like microsurgical tools for minimal tissue trauma, piezoelectric devices for precise bone modification, and enhanced visualization systems, have revolutionized the procedure, making it more precise and predictable.
Alternative Treatments and Prevention
While pocket reduction surgery provides excellent results in many cases, alternative treatments may be appropriate for some patients. These options include intensive periodontal maintenance, locally administered antibiotics, and laser therapy. In most situations, the choice between surgical and non-surgical approaches depends on disease severity, patient preference, medical history, and financial considerations.
Prevention is the best approach to periodontal disease. A comprehensive prevention strategy that includes good daily oral hygiene, regular professional cleanings, prompt attention to early warning signs, and management of risk factors minimizes the risk of developing severe periodontal disease.
Making an Informed Decision
Deciding whether to undergo pocket reduction surgery requires careful consideration. Before deciding, make sure you understand the expected results, recovery timeline, potential risks and complications, and consequences of delayed treatment. Proper preparation includes gathering information about the procedure, discussing concerns with your dental team, reviewing post-operative instructions, and planning for recovery time.
Successful treatment requires a partnership between the patient and provider that combines surgical expertise with dedicated home care. By understanding the procedure, its benefits, and the factors that influence success, you can confidently determine whether pocket surgery is right for you. Your dental team can also answer your questions and help you make a good decision.
Closing Thoughts
If you notice signs of periodontal disease or have concerns about your gum health, schedule a consultation with a periodontal specialist to discuss your treatment options. Prompt treatment improves treatment outcomes, so be sure to see a professional as soon as possible. A vibrant, healthy smile awaits!